Analysis of the Influence of Competency and Workload on Employee Performance with Presenteism as An Intervening Variable in the Distribution Regulation Implementing Unit (UP2D) PT. PLN (Persero) North Sumatera Distribution Main Unit
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.47353/ijema.v2i9.242Keywords:
competence, workload, presenteeism, employee performance, PT. PLN (Persero)Abstract
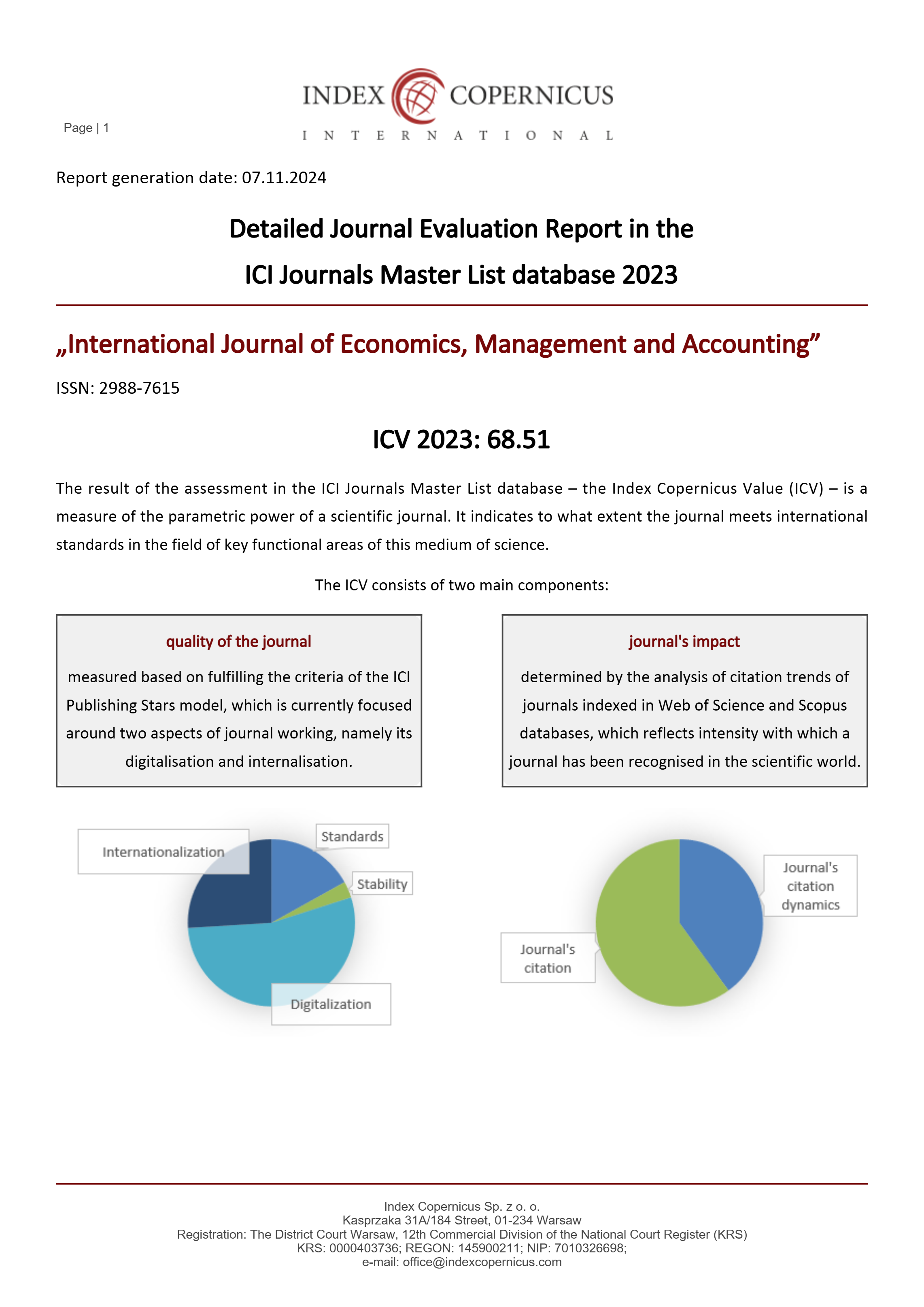
This study aims to analyze the influence of competence and workload on employee performance with presenteeism as an intervening variable at the Distribution Management Implementation Unit (UP2D) of PT. PLN (Persero) North Sumatra Distribution Main Unit. Competence and workload are important factors that influence employee performance in achieving organizational goals, while presenteeism, which refers to the physical presence of employees without optimal productivity, can be a barrier to performance. This study uses a quantitative approach with an explanatory research design. Data were collected through questionnaires distributed to employees of UP2D PT. PLN (Persero), and analyzed using the path analysis method to measure the direct and indirect relationships between the variables studied. The results of this study are that Workload has a negative and significant effect on Employee Performance with an original sample value of -0.264 and p values 0.006. Workload has a positive and significant effect on Presenteeism with an original value of 0.379 and p values 0.000. Competence has a positive and significant effect on Employee Performance with an original sample value of 0.300 and p values of 0.001. Competence has a negative and significant effect on Presenteeism with an original sample value of -0.579 and p values of 0.000. Presenteeism has a negative and significant effect on Employee Performance with an original sample value of -0.397 and p values of 0.002. Workload has a negative and significant effect on Employee Performance through Presenteeism with an original sample value of -0.151 and p values of 0.004. Competence has a positive and significant effect on Employee Performance through Presenteeism with an original sample value of 0.230 and p values of 0.008.
Downloads
References
Aboagye, E. et al. (2019) ‘Exhaustion and Impaired Work Performance in the Workplace: Associations with Presenteeism and Absenteeism’, Journal of Occupational and Presenteeism as a global phenomenon: Unraveling the psychosocial mechanisms from the perspective of social cognitive theory’, Cross Cultural and Strategic Management, 23(2), pp. 216–231. doi: 10.1108/CCSM-09- 2015-0106/FULL/XML.
Cooper, C. L., & Lu, L. (2018). Presenteeism at Work. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Fahmi, Irham. 2017. Manajemen Sumber Daya Manusia. Alfabeta, Bandung
Ghozali, Imam. (2018). Structural Equation Modeling Metode Alternatif dengan Partial Least Square (PLS) Edisi 4. Universitas Diponegoro, Semarang.
Koesomowidjojo, Suci (2017). Panduan Praktis Menyusun Analisis Beban Kerja. Jakarta: Raih Asa Sukses
Pramularso, E.Y. 2018. “Pengaruh Kompetensi Terhadap Kinerja Karyawan CV Inaura Anugerah Jakarta”. Widya Cipta. Vol. II, No. 1.
Rahmat, S. N. (2019). Pengaruh Kompetensi, Kompensasi Dan Disiplin Kerja Terhadap Kinerja Pegawai Badan Pendapatan Daerah Kota Makassar. PARADOKS: Jurnal Ilmu Ekonomi, 121-132.
Rachmaniza, Shafira. (2020). Pengaruh Kompetensi dan Komitmen Organisasi terhadap Kinerja Karyawan pada Divisi Produksi di PT. Sinar Ragamindo Utama Bandung. Prosiding Manajemen, 6(1)
Mangkunegara. 2017. Manajemen Sumber Daya Manusia Perusahaan, Bandung : Remaja Rosdakarya.
McGregor, A. M. (2016). A job demands-resources approach to presenteeism. Journal Career Development International, Vol. 21 Iss 4 .
Rohman, & Ichsan. (2021). Pengaruh Beban Kerja dan stress Kerja Terhadap Kinerja Karyawan PT Honda Daya Anugrah Mandiri Cabang Sukabumi. 2(1), 1–22.
Rusvitawati, Devi et al. 2019. “Pengaruh Kompetensi Terhadap Kinerja Karyawan Rumah Sakit Sari Mulia Banjarmasin.” Jurnal Wawasan Manajemen 7(1):1–16.
Sugiyono. (2016). Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif, Kualitatif dan R&D, Cetakan ke-24. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Afif Yasri, Syahrizal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.