The Effect of Brand Hate on Non-repurchase Intention with Variety Seeking Behavior as Moderating Variable
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.47353/ijema.v1i5.62Keywords:
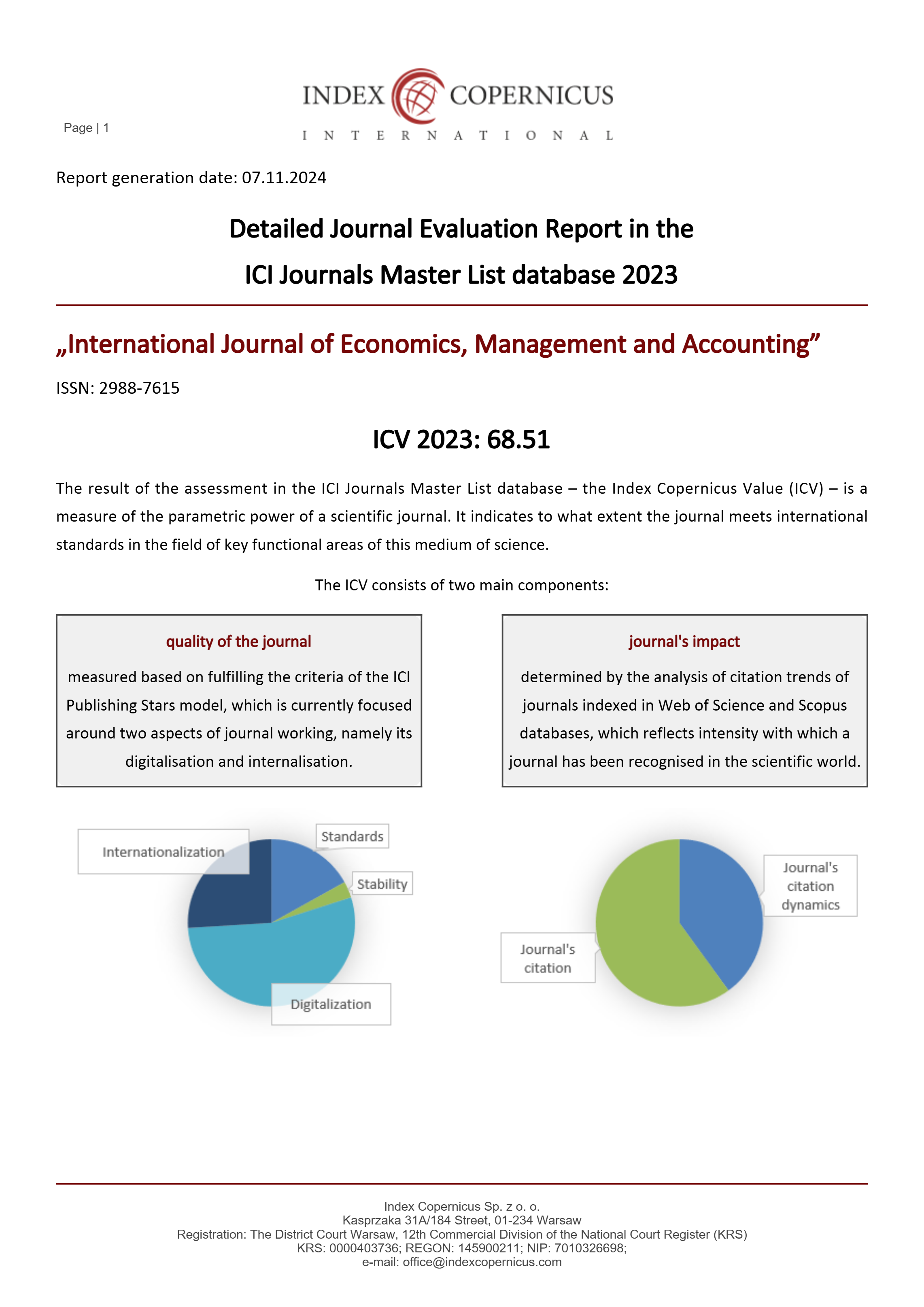
Brand hate, online complaining, negative word of mouth, non-repurchase intention, variety seeking behaviorAbstract
The purpose of this study is to examine the relationship between brands and consumers in a negative perspective that focuses on consumer behavior, such as purchase decisions by contributing to adding variables that can moderate the relationship between brand hate and non-repurchase intention, namely variety seeking behavior. The existence of a tendency for people to choose variety makes it important for researchers to use the variable seeking behavior to see its moderating effect on the non-repurchase intention. The population used in this study are e-commerce users in the five major cities in Indonesia. The sample selection technique uses purposive sampling. Data were collected through survey shared by Sosial Media. Data is processed using SMART-PLS 3.2.9. The results shows that brand hate has a positive effect on NWOM, Online Complaining and Non-repurchase intention. NWOM has a positive effect on non-repurchase intention. Online complaining has no effect on non-repurchase intention. Variety seeking behavior does not moderate the relationship between brand hate, NWOM, online complaining and non-repurchase intention.
Downloads
References
Bijmolt, T. H. A., Huizingh, E. K. R. E., & Krawczyk, A. (2014). Effects of complaint behaviour and service recovery satisfaction on consumer intentions to repurchase on the internet. Internet Research, 24(5), 608–628. https://doi.org/10.1108/IntR-03-2012-0056
Bryson, D., & Atwal, G. (2019). Brand hate: the case of Starbucks in France. British Food Journal, 121(1), 172–182. https://doi.org/10.1108/BFJ-03-2018-0194
Bryson, D., Atwal, G., & Hulten, P. (2013). Towards the conseptualisation of the antecedents of extreme negative affect towards luxury brands. Qual. Mark. Res. Int, 16, 393–405.
Curina, I., Francioni, B., Hegner, S. M., & Cioppi, M. (2020). Brand hate and non-repurchase intention: A service context perspective in a cross-channel setting. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 54(January 2019), 102031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2019.102031
Davvetas, V., & Diamantopoulos, A. (2017). “Regretting your brand-self?” The moderating role of consumer-brand identification on consumer responses to purchase regret. Journal of Business Reseacrh, 80, 218–227. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2017.04.008
Goetzinger, L., Park, jung kun, & Widdows, R. (2006). E‐customers’ third party complaining and complimenting behavior. International of Service Industry Management, 17(2), 193–206. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1108/09564230610656999
Grégoire, Y., Tripp, T., & Legoux, R. (2009). When Customer Love Turns into Lasting Hate: The Effects of Relationship Strength and Time on Customer Revenge and Avoidance. Journal of Marketing, 73(6), 18–32. https://doi.org/10.1509/jmkg.73.6.18
Hegner, S., Fetscherin, M., & Delzen, M. Van. (2017). Determinants and Outcomes of Brand Hate. J. Prod. Brand Manag, 26, 13–25.
Istanbulluoglu, D., Leek, S., & Szmigin, I. T. (2017a). Beyond exit and voice: developing an integrated taxonomy of consumer complaining behaviour. European Journal of Marketing, 51(5–6), 1109–1128. https://doi.org/10.1108/EJM-04-2016-0204
Istanbulluoglu, D., Leek, S., & Szmigin, I. T. (2017b). Beyond exit and voice: developing an integrated taxonomy of consumer complaining behaviour. European Journal of Marketing, 51(5–6), 1109–1128. https://doi.org/10.1108/EJM-04-2016-0204
Japutra, A., Ekinci, Y., & Simkin, L. (2018). Positive and negative behaviours resulting from brand attachment: The moderating effects of attachment styles. European Journal of Marketing, 52(5–6), 1185–1202. https://doi.org/10.1108/EJM-10-2016-0566
Jayasimha, K. R., Chaudhary, H., & Chauhan, A. (2017). Investigating consumer advocacy, community usefulness, and brand avoidance. Marketing Intelligence and Planning, 35(4), 488–509. https://doi.org/10.1108/MIP-09-2016-0175
Johnson, A. R., Matear, M., & Thomson, M. (2011). A coal in the heart: self relevance as a post-exit predictor of consumer anti-brand actions. J. Consum, 38, 108–125.
Kotler, P., & Keller, K. L. (2016). Marketing Management MARKETING MANAGEMENT Marketing Management. In Marketing Management.
Kucuk, S. U. (2018). Macro-level antecedents of consumer brand hate. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 35(5), 555–564. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1108/JCM-10-2017-2389
Liao, T., & Keng, C. (2013). Online shopping delivery delay: Finding a psychological recovery strategy by online consumer experiences. Computers in Human Behavior, 29(4), 1849–1861. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2013.03.004
McAlister, L. (1982). A dynamic attribute satiation model of variety-seeking behavior. J. Consum1, 141–150. https://doi.org/10.1086/208907
Piyush, S., Bharadhwajh, S., & Roger, M. (2009). Impulse buying and variety seeking: A trait-correlates perspective. Elsevier, Inc.
Ridhah, H. (2022). Penerapan Manajemen Syariah Pada Lembaga Keuangan Mikro Syariah Semasa Pandemi Covid-19. Equilibria Pendidikan: Jurnal Ilmiah Pendidikan Ekonomi, 7(1), 1-7.
Sekaran, U., & Bougie. (2016). Research Methods for Business: a skill building approach Seventh Edition. Wiley.
Sulistyaningrum, D. (2012). Pengaruh Brand Loyalty Terhadap Variety Seeking. Journal of Social and Industrial Psychology, 1.
Zarantonello, L., Romani, S., Grappi, S., & Fetscherin, M. (2016). Brand Hate. Journal of Brand Management, 25(1), 549–560. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1057/s41262-018-0105-5
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Syahrinabila Pulungan, Teguh Widodo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.