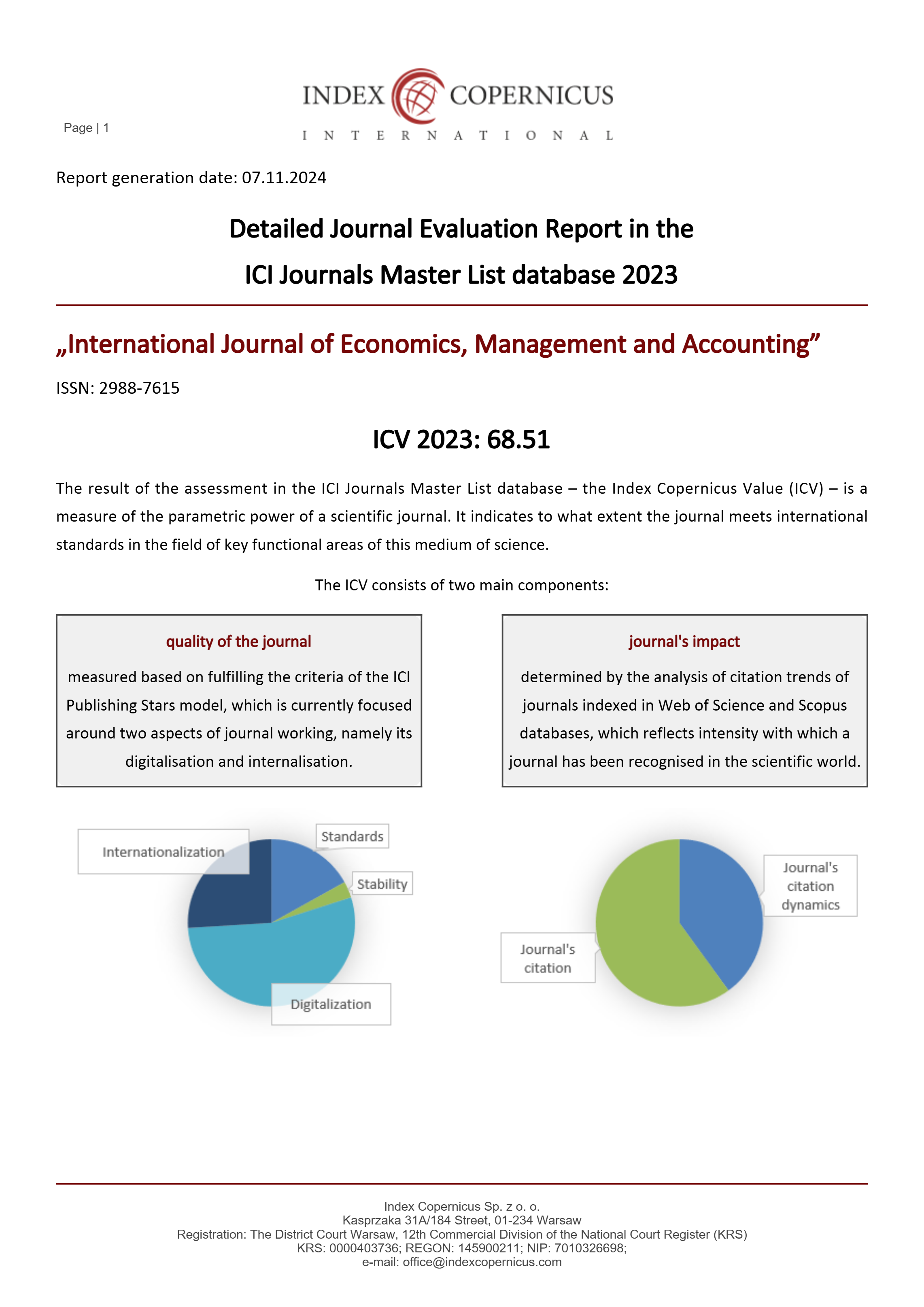
The Influence of Motivation and Work Discipline on Employee Performance with the Level of Employee Satisfaction as an Intervening Variable at BPJS Pematang Siantar Branch Office and Padang Sidimpuan Branch Office
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.47353/ijema.v2i2.171Keywords:
Motivation, Work Discipline, Job Satisfaction, Employee PerformanceAbstract
This research is to look at the influence of motivation, work discipline, and job satisfaction on employee performance. The phenomenon that occurs at the BPJS Employment Pematang Siantar and Padang Sidimpuan Branch Offices is that the motivation given sometimes does not work for employees, it is only used as a formality for employees but is not carried out by employees, many employees are also undisciplined due to time problems and also work so that employee performance will not be optimal if employees do not comply with regulations, this occurs due to the employee's lack of satisfaction with the organization which does not pay attention to and improve the welfare of its employees so that employees prefer to work according to the standard and do not show their commitment to the organization. The results of this research are as follows: Work Discipline has a positive and significant effect on Employee Job Satisfaction with a value of 0.750 and a value of 0.000 <0.05. Work Discipline has a positive and significant effect on Employee Performance with a value of 0.406 and a value of 0.005 <0.005. Employee Job Satisfaction has a positive and significant effect on Employee Performance with a value of 0.361 and a value of 0.011 <0.05. Motivation has a positive and significant effect on Employee Job Satisfaction with a value of 220 and a value of 0.005. Motivation has a positive and significant effect on employee performance with a value of 0.210 and a value of 0.016 <0.05. Work Discipline has a positive and significant indirect effect on Employee Performance through Employee Job Satisfaction with a value of 0.271 and a value of 0.022. Motivation has a positive and significant indirect effect on employee performance through employee job satisfaction with a value of 0.079 and a value of 0.038.
Downloads
References
Anwar Prabu Mangkunegara, A. A. (2017). Manajemen Sumber Daya Manusia Perusahaan. Bandung: Remaja Rosdakarya.
Agustini, N. K. I., & Dewi, A. S. K. (2019). Pengaruh Kompensasi, Disiplin Kerja dan Motivasi terhadap Produktivitas Karyawan. E-Jurnal Manajemen, 8(1), 231-258.
Ayunira, P. (2020). Analisis Perbandingan Kinerja Keuangan Bank Aceh Syariah Sebelum dan Sesudah Konversi. Fakultas Ekonomi dan Bisnis, Universitas Islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah, Skripsi diterbitkan.
Arikunto, S. (2015). Prosedur Penelitian Suatu Pendekatan Praktik. Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
Arikunto, S. (2017). Pengembangan Instrumen Penelitian dan Penilaian Program. Yogyakarta: Pustaka Pelajar.
Enny, M. (2019). Manajemen Sumber Daya Manusia. Surabaya: UBHARA Management Press.
Ghozali, I., & Latan, H. (2014). Partial Least Squares: Konsep, Teknik dan Aplikasi Menggunakan SmartPLS 3.0 (Edisi ke-2). Semarang: Universitas Diponegoro.
Hasibuan, M. S. P. (2017). Manajemen Sumber Daya Manusia. Edisi Revisi. Jakarta: Bumi Aksara.
Umar, H. (2014). Metode Penelitian untuk Skripsi dan Tesis. Jakarta: Rajawali.
Nurjaya, N. (2021). Pengaruh Disiplin Kerja, Lingkungan Kerja dan Motivasi Kerja terhadap Kinerja Karyawan di PT. Hazara Cipta Pesona. Jurnal Ilmiah Nasional, III(1), 60-74.
Paramita, R. W. D. (2021). Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif. Lumajang: Widya Gama Press.
Russiadi, et al. (2016). Memahami Pendekatan Kuantitatif. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Siyoto, S., & Sodik, A. (2015). Dasar Metodologi Penelitian. Yogyakarta: Literasi Media Publishing.
Wibowo, et al. (2015). Pendidikan Karakter Berbasis Kearifan Lokal di Sekolah (Konsep, Strategi dan Implementasi). Yogyakarta: Pustaka Pelajar.
Yohanson, A. K., Lukmanul Hakim, dan Alimuddin. (2021). Pengaruh Gaya Kepemimpinan dan Motivasi Kerja terhadap Kinerja Karyawan PT. Japfa Comfeed Indonesia TBK, Cabang Tanggamus. Science Economies: Jurnal Ekonomi, Keuangan dan Bisnis, 6(2), 143-148.
Yuniarsih, T. (2017). Kinerja Unggul Sumber Daya Manusia. Bandung: Rizky Press.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Bastian Amat Hasudungan Simanjuntak, Muhammad Isa Indrawan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.