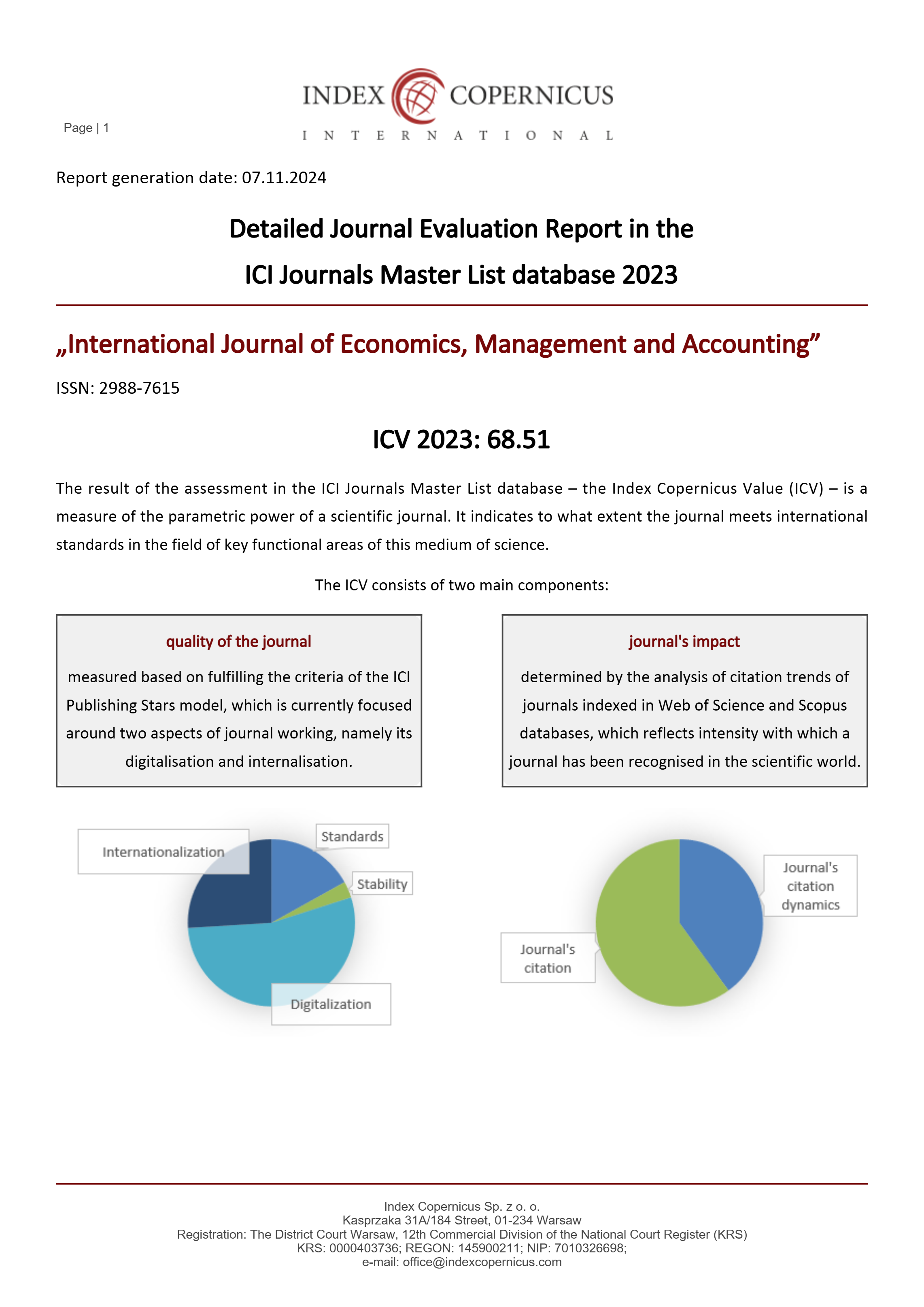
Analysis of the Influence of Government Expenditures in the Education, Health and Infrastructure Sectors on Economic Growth in Lampung Province
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.47353/ijema.v1i4.53Keywords:
government spending, education, health, infrastructure, economic growthAbstract
This research aims to analyze the influence of government spending in the education, health and infrastructure sectors on economic growth in Lampung Province in 2014 - 2021. The analytical method used in this research is panel data regression analysis with the help of Eviews software. Statistical tests used in this research include classical assumption tests (normality test, multicollinearity test, heteroscedasticity test, autocorrelation test), t test, f test, and coefficient of determination test. The results of this research show that: (1) government spending in the education sector partially has a positive and significant effect on economic growth in Lampung Province, (2) government spending in the health sector partially has a positive and significant effect on economic growth in Lampung Province, (3) spending government infrastructure sector partially has a positive and significant effect on economic growth in Lampung Province, (4) government spending in the education, health and infrastructure sectors simultaneously or together has a significant effect on economic growth in Lampung Province.
Downloads
References
Abimanyu Y. (2015). Pengeluaran Pemerintah dan Impaknya terhadap Pertumbuhan Ekonomi. 1 – 25
Agus Widarjono. (2018). EKONOMETRIKA: Pengantar dan Aplikasinya Disertai Panduan EViews (Kelima). UPP STIM YKPN. Yogyakarta. 381 hlm.
Aida, N., Afif, F., & Peni, T. (2021, May 25). Krisis Global dan Pertumbuhan Ekonomi di Indonesia. Jurnal Ekonomi Pembangunan, 10(1), 46-55.
Ambya. (2020). How Government Spending on Public Sector Affect The Economic Growth? Journal of Economics and Policy. 13(1), 218–229.
Ambya, A., & Ciptawaty, U. (2022). Hubungan antara belanja pemerintah, tingkat kemiskinan, dan pertumbuhan ekonomi daerah otonomi baru di Provinsi Lampung. Jurnal Paradigma Ekonomika, 17(1), 157-166.
Badan Pusat Statistik (2016). Statistik Keuangan Daerah 2015. Provinsi Lampung: Badan Pusat Statistik.
Badan Pusat Statistik (2017). Statistik Keuangan Daerah 2016. Provinsi Lampung: Badan Pusat Statistik.
Badan Pusat Statistik (2018). Statistik Keuangan Daerah 2017. Provinsi Lampung: Badan Pusat Statistik.
Badan Pusat Statistik (2019). Statistik Keuangan Daerah 2018. Provinsi Lampung: Badan Pusat Statistik.
Badan Pusat Statistik (2020). Statistik Keuangan Daerah 2019. Provinsi Lampung: Badan Pusat Statistik.
Badan Pusat Statistik (2021). Statistik Keuangan Daerah 2020. Provinsi Lampung: Badan Pusat Statistik
Balaj, D., & Lani, L. (2017). The Impact of Public Expenditure on Economic Growth of Kosovo. Journal of Economics. 13(5), 401–412.
Basuki, A. T. R. I., & Yuliadi, I. (2015). Electronic data processing (Pertama). Danisa Media.
Beylik, U., Cirakli, U., Cetin, M., & Ecevit, E. (n.d.). The relationship between health expenditure indicators and economic growth in OECD countries : A Driscoll-Kraay approach.
Bhat, K., & Yan, C. (2017). Public Spending and Economic Growth : Empirical Investigation in the Context of Pakistan. Journal of Economics and Sustainable Development. 8(17).
Guritno Mangkoesoebroto. (1993). Ekonomi Publik (Ketiga). BPFE-Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta. 295 hlm.
Komang, I. G., Dianaputra, A., & Aswitari, L. P. (2015). Pengaruh Pembiayaan Pemerintah di Sektor Pendidikan dan Kesehatan Terhadap Indeks Kualitas Manusia serta Pertumbuhan Ekonomi pada Kabupaten/Kota Provinsi Bali Tahun 2011 - 2015. Jurnal Ekonomi Pembangunan. 286–311.
Lestari, N. I. (2010). The effect of government education spending on economic growth through school enrollment in indonesia. 1995, 109–122.
Lim, B., Kim, H. S., & Park, J. (2020). Direct E ff ect of TC on the LME Copper Prices. 1986, 1–9.
Mercan, M., & Sezer, S. (2014). The effect of education expenditure on economic growth : The case of Turkey. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 109, 925–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2013.12.565.
Michael P. Todaro dan Stephen C. Smith. (2011). Pembangunan Ekonomi (Kesebelas). Penerbit Erlangga. Jakarta. 518 hlm.
O, K. R., A, B. H., Gbenga, A., & O, B. N. (2014). The Impact of Public Sector Spending on Economic Growth of Nigeria. Journal of Economics and Sustainable Development. 5(3), 216–224.
Olivier Blanchard dan David R. Johnson. (2017). MAKROEKONOMI (Keenam). Penerbit Erlangga. Jakarta. 597 hlm.
OTIWU, K. ., CHUKWU, L. ., & OKERE, P. . (2018). The Effect of Public Expenditure on the Economic Growth in Nigeria (1980 - 2013). Journal of Economics and Sustainable Development. 1700, 87–96.
Puspitasari, J. M., & Sarfiah, S. N. (2017). Analisis Pengaruh Pengeluaran Pemerintah di Sektor Pendidikan, Sektor Kesehatan, Sektor Infrastruktur Terhadap Pertumbuhan Ekonomi di Indonesia (Periode Tahun 2010 - 2017). Journal of Economic .
Randolph, Raquel (2020). Does Education Expenditure have a Positive Impact on Economic Growth? A Panel Data Estimation of Five Developing Countries. Journal of Economics.
Rizvi, S. A. F. (2019). Health Expenditures , Institutional Quality and Economic Growth. Empirical Economic Review. 2(1), 63-82.
Rokhmat, A., Sasana, H., SBM, N., & Yusuf, E. (2020). Analisis Pengaruh Pembangunan Infrastruktur Pelayanan Dasar, Jalan Provinsi, Air Bersih, Hotel, Penginapan, dan Restoran Terhadap Produk Domestik Regional Bruto. Jurnal Riset Ekonomi dan Bisnis. 13(2), 70–88.
Sukirno, S. (2013). MAKROEKONOMI: Teori Pengantar (Ketiga). Rajawali Pers. Jakarta. 451 hlm.
Sasongko, H., Ilmiyono, A. F., & Aldillah, Z. H. (2019). Pengaruh Pengeluaran Pemerintah Bidang Pendidikan dan Kesehatan Terhadap Pertumbuhan Ekonomi di Provinsi Jawa Barat Tahun 2016 - 2019. Jurnal Akunida. 1, 12–29.
Taufiq, I., Anderson, K. G., & Agnes, L. C. P. L. (2021). Analisis Pengaruh Belanja Daerah dan Indeks Pembangunan Manusia Terhadap Pertumbuhan Ekonomi Kabupaten dan Kota di Bolaang Mongondow Raya. Jurnal Pembangunan Ekonomi dan Keuangan Daerah. 5, 75-95.
Yuliawan, D. (2015). Analisis Rencana Pembangunan Kawasan Agropolitan (studi kasus Kecamatan Banjit Kabupaten Way Kanan). JEP, 4(0), 49.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Tarisa Yuwan Azzahra, Ambya

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.